Explain Ethereum Blockchain Platform Architecture With Block Diagram
As explain ethereum blockchain platform architecture with block diagram takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a fascinating exploration of how Ethereum’s unique framework empowers decentralized applications and smart contracts.
Ethereum stands out in the blockchain world, not just for its innovative approach to decentralization but also for the powerful tools it provides to developers and users alike. This overview will delve into the architecture that supports Ethereum, illustrating its components and the critical roles they play through a detailed block diagram.
Overview of Ethereum Blockchain
Ethereum is a decentralized platform that utilizes blockchain technology to enable developers to build and deploy applications, particularly those that require smart contracts. A blockchain is essentially a distributed ledger that records transactions across many computers, ensuring that the data is secure and immutable. Ethereum revolutionizes this concept by not only allowing the transfer of value but also providing a robust framework for creating decentralized applications (dApps) and executing self-enforcing contracts.The significance of Ethereum lies in its ability to facilitate a trustless environment where parties can interact without the need for a central authority.
Unlike traditional blockchain platforms, Ethereum stands out due to its flexibility and extensive capabilities. Its support for smart contracts allows for automated execution of agreements, opening up numerous possibilities for innovation across various sectors.
Ethereum Blockchain Architecture

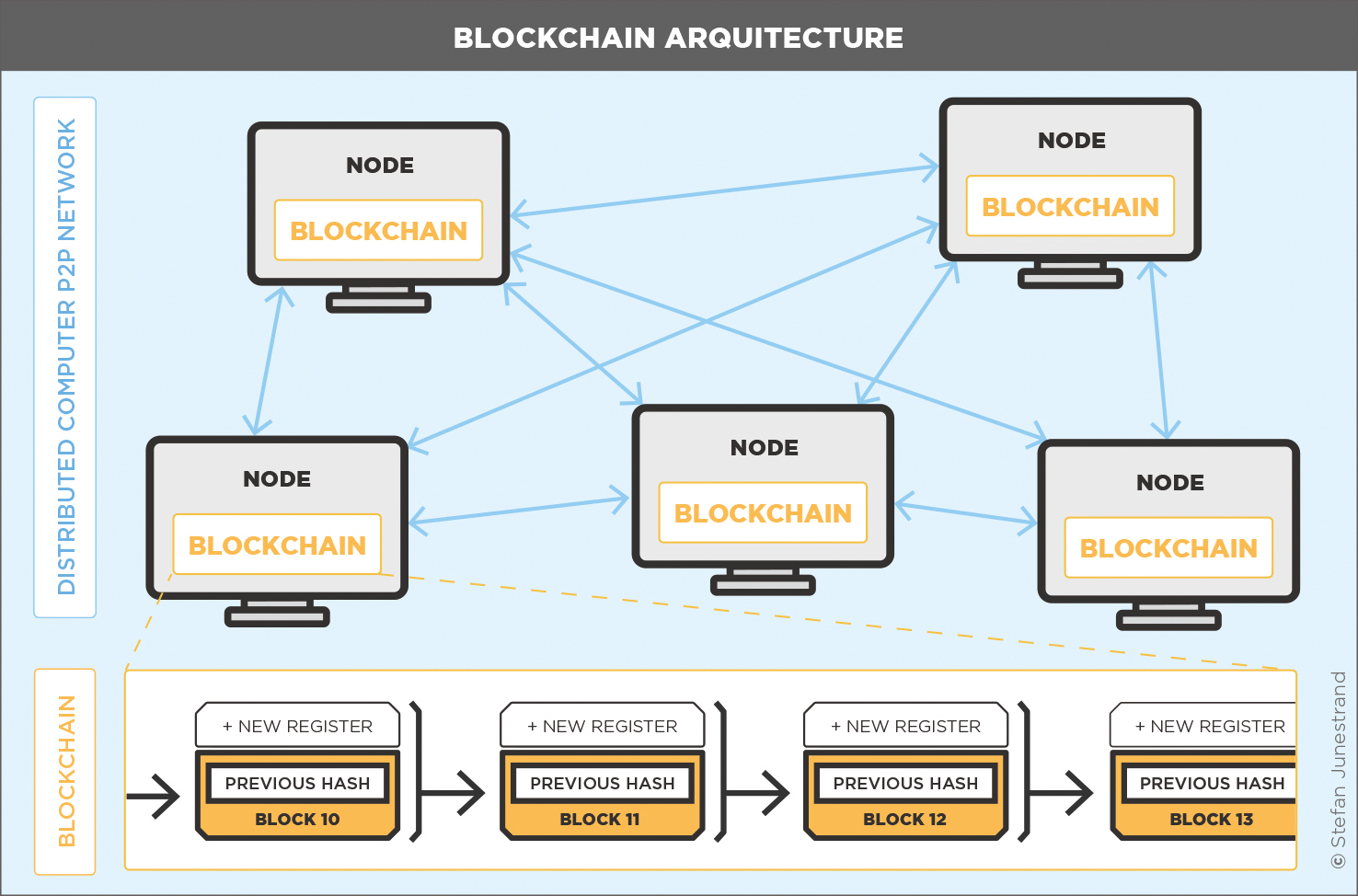
The architecture of the Ethereum blockchain is composed of multiple layers, each playing a vital role in its operation. At its core, Ethereum consists of a peer-to-peer network where nodes communicate to process transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain. The fundamental components include:
- Nodes: The computers that maintain the Ethereum network, each holding a copy of the blockchain.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): The runtime environment for executing smart contracts.
To illustrate this structure, a block diagram can be used to showcase the relationship between nodes, smart contracts, and the EVM. Each component works in unison to ensure the functionality and security of the Ethereum network.
Nodes in Ethereum
In the Ethereum ecosystem, there are different types of nodes, each serving specific roles. The primary types include:
- Full Nodes: These nodes store the entire blockchain and are responsible for validating transactions and blocks. They provide the backbone of the Ethereum network.
- Light Nodes: These nodes only download the header of the blockchain and rely on full nodes for transaction verification, making them less resource-intensive.
A comparison table of node types is as follows:
| Node Type | Function | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Full Node | Validates transactions and maintains a complete blockchain copy | High storage and bandwidth |
| Light Node | Verifies transactions with minimal data | Low storage and bandwidth |
Smart Contracts
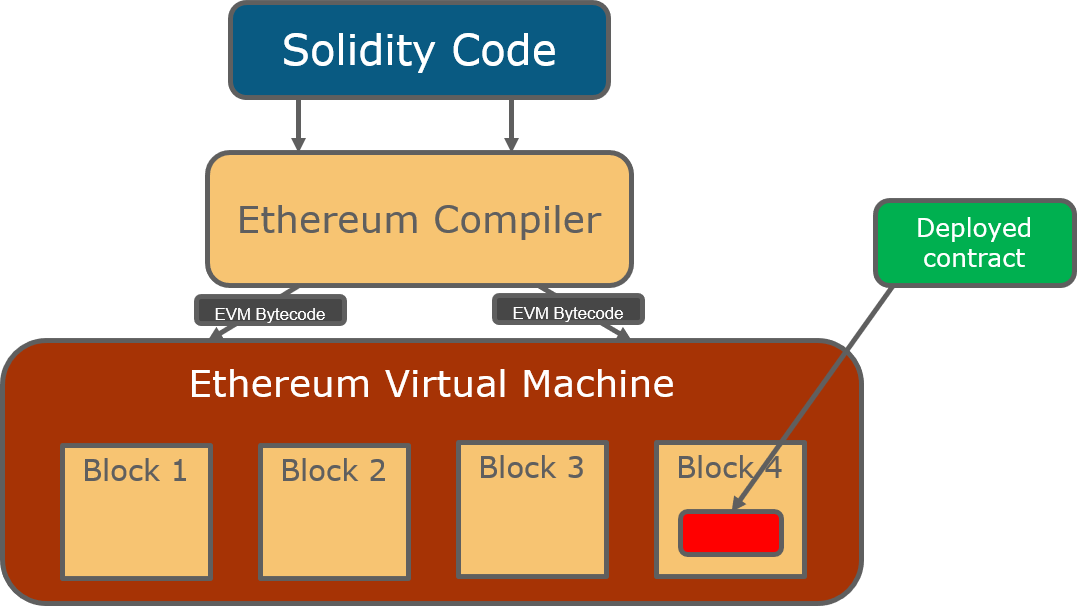
Smart contracts are a defining feature of the Ethereum platform, allowing for automated and trustless transactions. These contracts are essentially programs that execute predefined conditions without human intervention. Writing smart contracts involves using a programming language called Solidity, which is specifically designed for Ethereum.Deploying smart contracts is a straightforward process, involving the compilation of code and sending it to the Ethereum network as a transaction.
Once deployed, these contracts can interact with each other or dApps, enabling a wide range of functionalities. Examples of use cases for smart contracts include:
- Insurance claims processing
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications
- Supply chain management
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is crucial for executing smart contracts. It acts as a decentralized computing environment that allows all Ethereum nodes to execute contract code in a consistent manner. The EVM ensures that the outcomes of smart contracts are the same regardless of where they are executed across the network.Key features of the EVM include:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Decentralization | Operates on a peer-to-peer network of nodes |
| Security | Inherently secure due to its distributed nature |
| Interoperability | Facilitates interaction between different smart contracts |
Consensus Mechanism
Ethereum originally employed a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW), which required miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. However, Ethereum is in the process of transitioning to Proof of Stake (PoS), a system that allows validators to create and validate new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.This transition is important because PoS is expected to improve the network’s efficiency and energy consumption while maintaining security.
While PoW relies on computational power, PoS emphasizes economic incentives, making it more accessible to more users.
Token Standards
Ethereum supports various token standards that facilitate the creation and management of tokens on its platform. The most notable standards include ERC-20, which is used for fungible tokens, and ERC-721, which is used for non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Projects utilizing these standards have transformed various industries, such as gaming, art, and finance, exemplifying the versatility of Ethereum’s architecture. Token standards are essential for the development of decentralized applications (dApps), allowing developers to create interoperable and flexible solutions.
Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Decentralized applications (dApps) are applications that run on the Ethereum blockchain, leveraging smart contracts for functionality. These applications can vary widely in purpose, from gaming to financial services. The architecture of dApps typically includes a frontend user interface that interacts with smart contracts on the backend.Popular examples of dApps include:
- Uniswap – A decentralized exchange for swapping tokens
- CryptoKitties – A game based on the breeding and trading of virtual cats
- Chainlink – A decentralized oracle network providing real-world data to smart contracts
Security Considerations
Developers on the Ethereum platform face several security challenges, such as vulnerabilities in smart contracts that can lead to exploits and financial losses. To mitigate these risks, developers should follow best practices, including:
- Conducting thorough testing and audits of smart contracts
- Implementing fail-safes and emergency protocols
- Keeping up-to-date with security updates and community resources
Security tools and resources available for Ethereum developers include:
- MythX – A security analysis tool for smart contracts
- OpenZeppelin – A library of secure smart contract templates and utilities
- Slither – A static analysis framework for Solidity smart contracts
Closing Summary
In summary, understanding the architecture of the Ethereum blockchain provides invaluable insights into its functionality and capabilities. As we continue to explore the evolving landscape of decentralized technologies, the principles and designs behind Ethereum remain crucial for developers, businesses, and enthusiasts alike, paving the way for innovative applications that reshape various industries.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of Ethereum?
Ethereum allows developers to create decentralized applications using smart contracts, enhancing transparency and reducing reliance on central authorities.
How does Ethereum’s consensus mechanism work?
Ethereum utilizes a consensus mechanism to validate transactions and blocks, transitioning from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake for improved efficiency and security.
What are smart contracts and how do they function?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, executing automatically once conditions are met.
What differentiates Ethereum from Bitcoin?
While Bitcoin is primarily a digital currency, Ethereum serves as a platform for decentralized applications and smart contracts, offering broader functionalities.
What security measures should developers consider on Ethereum?
Developers should follow best practices such as thorough testing, auditing smart contracts, and employing security tools to mitigate risks of vulnerabilities.

